Application of Computers in Accounting Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 12
Application of Computers in Accounting Class 11 Introduction
In Class 11,the study of the application of computers in accounting introduces students to the transformative role technology plays in the field of accounting. This subject explores how computer systems streamline financial processes, enhance accuracy, and facilitate efficient data management within the realm of financial accounting and reporting.
Application of Computers in Accounting Class 11 Definition
The application of computers in accounting at the Class 11 level involves utilizing computer technology to automate and streamline various accounting processes, enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and data management in financial record-keeping.
Application of Computers in Accounting Class 11 Important Notes
- Automation of Transactions:
- Computers automate routine accounting tasks such as data entry, ledger maintenance, and transaction processing, reducing manual effort and minimizing errors.
- Accounting Software:
- Specialized accounting software like Tally, QuickBooks, and others are extensively used to manage financial transactions, generate reports, and ensure compliance with accounting standards.
- Data Accuracy and Integrity:
- Computers enhance accuracy by performing calculations swiftly and minimizing the risk of human error, ensuring the integrity of financial data.
- Real-time Financial Reporting:
- Computers enable real-time generation of financial statements, providing instant access to critical financial information for decision-making.
- Database Management:
- Databases in accounting systems efficiently store and retrieve vast amounts of financial data, ensuring organized and secure data management.
- Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT):
- Computers facilitate EFT for seamless and quick transfer of funds, reducing the reliance on traditional paper-based transactions.
- Security Measures:
- Implementing robust security measures, such as encryption and access controls, is crucial to safeguard financial data from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
- Audit Trail:
- Accounting systems maintain an audit trail, documenting every transaction and modification, aiding in accountability, transparency, and audit processes.
- Integration with Other Systems:
- Computers allow integration with various business systems, creating a cohesive network where financial data can be shared seamlessly across different departments.
- Compliance with Regulations:
- Accounting software helps in ensuring compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, automating the process of adhering to tax laws and accounting standards.
- User Training:
- Adequate training in using accounting software is essential for accounting professionals to leverage the full potential of computer applications and ensure efficient utilization.
Application of Computers in Accounting Class 11 Question and Answer
Question:1 state the different elements of a computer system.
Answer
A computer system is mainly composed of the following six elements.
- Hardware-– It includes all the physical components of a computer such as, keyboard. monitor, processor, etc. these can be touched and a user inputs commands through the,
- software–It is referred to a set of the programs enables a computer to perform its tasks or commands give by the user.
- Operating system
- utility programs
- Application software
- Language processors
- system software
- connectivity software
- People— It constitutes the most important part of a computer system. it basically refers t the individuals or the users who interact with the computer through the use of hardware and software. the following are the people who are involved in a computer system.
- system analysis
- operator
- Programmers
- Procedures--A series of operations that are executed in a certain manner in order to achieve a desire set of results is known as ,,Procedurs” these are mainly following three types of precedures.
- Hardware-Oriented procedures
- software-oriented procedures
- Internal Procedures
- Date–The facts that are gathered and entered into a computer system is known as’date” It may comprise of numbers. text, graphics etc,
- Connectivity–This refers to the manner, in which computer system is connected to the other electronic, devices through telephone lines’ microwave transmission, satelite link, etc, is known as ‘connectivity”
Question:2 List the distinctive advantages of a computer system over a manual system.
Answer.
The following are some of the distinctive advantages of a computer system over a maual system.
- High speed
- Accuracy
- Reliability
- Versatility
- stroage
Question:3 Draw black diagram showing the main components of a computer.
Answer.

Question:4 Give three examples of a tranaction processing system.
Answer.
Transaction processing system (TPS) refers to a computerised system that records. processes, validates and strores routine transactions that occur in various functional areas of a business on daily basis. some of the examples of transaction processing system are enlisted as.
- Automatic Teller Machine (ATMs)–These are those machines that handle the bank transactions through the use of specialised computer program.
- Payroll Application –These are the application that help to execute payroll programs using terminal and online processing these are commonly used for preparing payroll or salary of the employees.
- Order processing--with the help of TPS applications, orders are collected from clients either manually or through mails and telephonic calls. thereafter, these orders are processed to initiate inocing, account receivables and inventory control processing these are now a day widely used in almost every spheres of business. such as a online purchasing of tickets. online booking. etc.
Question:5 what is Accounting Information system?
Answer: An Accounting Information System (AIS) is a structure that businesses use to collect, store, process, manage, and disseminate financial and accounting data. It combines both accounting and information technology to facilitate the efficient flow of financial information within an organization
Key components of an Accounting Information System include:
- Data Input:
- Involves the collection and input of financial data into the system. This can include transactions, invoices, receipts, and other relevant financial information.
- Processing:
- The system processes the input data to generate meaningful financial information. This may involve calculations, summarizations, and categorizations of financial transactions.
- Storage:
- AIS stores financial data in databases or other storage systems. This allows for easy retrieval and reference of historical financial information.
- Information Output:
- AIS produces various reports and financial statements that are useful for management, stakeholders, and regulatory authorities. Examples include balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements.
- Internal Controls:
- AIS includes mechanisms to ensure the integrity and security of financial data. Internal controls help prevent errors, fraud, and unauthorized access to sensitive financial information.
- Decision Support:
- AIS provides tools for decision support, enabling management to analyze financial data and make informed decisions. This can involve budgeting, forecasting, and financial modeling.
- Audit Trail:
- Maintaining an audit trail is a critical aspect of AIS. It documents and tracks changes to financial data, providing a transparent record for internal and external auditing purposes.
- Integration:
- AIS integrates with other business systems, such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, to ensure seamless communication and data exchange between different departments within an organization.
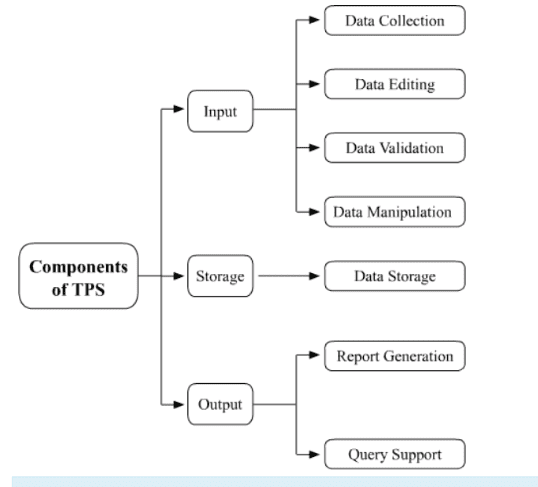
Question:6 Name three components of a transaction processing system.
Answer.
The Following are three main components of a transaction processing system (TPS)
- Input–A computerised accounting system acepts the complete transaction data as input through the process of data collection. data editing data validation and data manipulation.
- storage–The system stores the inputted data in computer storage media such as hard disk
- Output–The stored data, through the process of report generating and query support can be retrieved and processed as and when required for generating an accounting report as output.
Question:7 An organisation is a collection of interdependent decision-making units that exists to pursue organisational objectives. In the light of this statement, explain the relationship between information and decisions. also explain the role of transaction processing system faciliating the decision -making process in business organisation.
Answer: An organisation consists of various interprendent decision making units at every level of management and department. all these separate department take decisions for their, respective fields to achieve the desired common organisation objectives.
the organisation as a whole needs to set its targets. draft plans and formulate various policies these activities are based on the information (in form of data) regarding the past experiences and expected future conditions.
it is on the basis of this information that an organisation allocates its resources and attenmpts to accomplish its determined targets. thus it can be said that on one hand. information facilities the decision making process while on the other hand,
decisions took in the past acts as pool of information in the future. In this aspect Information form the most crucial part of today’s business environment In this context. Transaction processing system (TPS) has emerged as crucial component of the business operations.
transaction processing system (TPS) refers to a computerised system that records. processes validates and stores routine transactions that occur in various functional areas of business on daily basis. this system facilities the decision making in a business organisation through the following processes.
- Date collection— The TPS collects all the required data to complete one or more transactions. the data can be collected either manually or through other devices such as scanners and point of sale equipments.
- Date Editing– The system checks teh data for its accuracy, correctness and completeness.
- Data validation–It refers to a process, where TPS verifies the data for its correctness and rectifies the error. if detected.
- Date manipulation— TPS perfrom the process of calculation, then processes and analyses the inputted data on a pre-set design
- Date storage–It places or stores the data in one or more databse.
Conclusion
In Class 11, the study of the application of computers in accounting underscores the transformative role technology plays in streamlining financial processes, enhancing accuracy, and facilitating efficient data management within the realm of accounting, offering students a crucial insight into the modernization of financial record-keeping practices.
Glad to be one of many visitors on this awe inspiring internet site : D.
thanks