what is Company law In this Article we covered all the Important Topics related to company law read this article and understand what is company law we covered the introduction part and types of company law

Company law Introduction
The Industrial Revolution led to the emergence of large-scale business organizations these organizations require big investment and the risk involved is very high. limited resources and unlimited liabilities of partners are two important limitations of the partnership of partnership in undertaking big business.
What is company law?
Section 3 of the Companies Act. 1956 defines a company as ‘ a company formed and registered under this act or an existing company’ section 3 of the act states that ‘ an existing company means a company formed and registered under any of the previous companies laws’ this definition does not reveal the distinctive characteristics of a company.
According to the chief justice marshall of the USA ‘ A company is a person. artificial invisible intangible and existing only in the contemplation of the law. being a mere creature of law. it possesses only those properties which the character of its creation confers upon it either expressly or as incidental to its very existence
Company law notes
- Company law notes provide explanations of the legal rules and regulations that govern the operations of companies.
- They cover topics such as company formation, corporate structure, and the rights and responsibilities of directors and shareholders.
- Company law notes help individuals understand the legal framework surrounding businesses and corporations.
- They outline the rights and duties of various stakeholders, including shareholders, directors, and employees.
- These notes are beneficial for students studying business or law and professionals working in the corporate sector
Prospectus in company law
By law, a company prospectus is a document that companies use to explain their business and investment opportunities to potential investors. Contains information about the company’s operations, financial health, risks, and objectives.
This book helps investors make the right decisions about investing in company stocks or bonds. It serves as a guide that provides information about the company and its offerings to help investors understand what they are getting into before they decide to invest
Types of meeting in company law
Board Meetings: These are meetings of company directors to discuss various business matters and make decisions. Managers discuss strategy, financial information and other important issues related to the company’s operations.
General meetings: General meetings involve the members and are usually held annually. They provide members with updates on the company’s operations, finances and future plans. Shareholders also have the opportunity to vote on important matters, such as the election of the board of directors or changes to the company’s articles of association.
Ordinary general meeting: A general meeting is a special type of meeting that is held once a year. It is mandatory for listed companies and allows shareholders to ask questions, receive reports from directors, and vote on resolutions.
Extraordinary general meeting (AGE): An extraordinary general meeting is convened outside the annual calendar to deal with urgent matters that cannot wait until the next general meeting. These meetings can be convened by the board or requested by members
Company law Bare act
Establishment of a Company: The law lays down the requirements and registration process for starting a company.
Shareholder Rights: Shareholders have rights and responsibilities defined in the articles of association, which allow them to participate in the company’s affairs and make important decisions.
Duties of directors: Directors must fulfill certain duties towards the company, including acting honestly and with integrity.
Financial Reporting: The Companies Act regulates financial reporting including the preparation, audit and publication of financial statements.
Corporate Governance: Guidelines for corporate governance policies and practices promote transparency and accountability in corporate governance.
Mergers and Acquisitions: The law defines the procedures and legal requirements for mergers, acquisitions and consolidations.
Formation of company
The whole process of formation of a company is divided into four steps for convenience
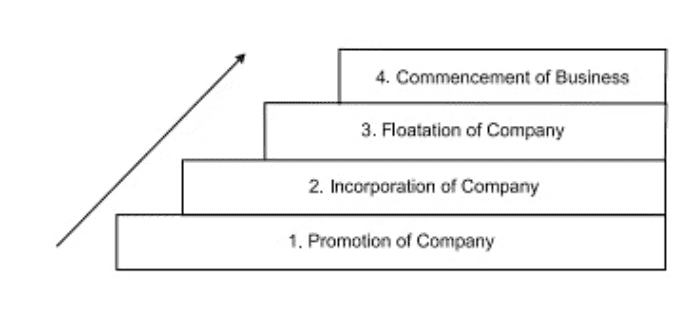
- Promotion of company
- Incorporation or registration of company
- Floatation of compmay
- Commencement of business
steps
1. Promotion of company
Promoter: is a person who initiates the process of formation of a company: he undertakes to form a company with references to a given project and takes the necessary steps to accomplish the purpose.
The promoter assumes responsibility for all the matters relating to the formation of the company.
2. Incorporation or registration of the company
It is for the legal process of forming a new company. This includes completing public documents and regulations to establish the company as a legal entity. Details such as company name, structure, directors, and members were clipped and recorded.
Company progress
3.Floatation of compmay
Floating a company usually involves making shares available for investors to buy on the stock exchange. This is similar to listing a company on a stock exchange and allowing individuals and organizations to buy and sell their shares. This is usually through an initial public offering (IPO), where shares are offered to the public for the first time To start a business
4. Commencement of business
Once the company is registered and all legal requirements are met, it can start operating. Opening a business simply means that the business begins activities such as selling products or providing services, generating revenue, and achieving creative goals.
Company Law Question and Answer
Question:1 Why is Company Law important?
Answer:
Legal Contracts: Corporate bylaws provide the legal framework that a company must follow in order to operate legally. It lays down rules on how companies are to be formed, managed, and dissolved.
Protection of shareholders: Corporate law protects the interests of various stakeholders of a company, including shareholders, directors, creditors, employees and the public. It defines their powers, duties and responsibilities.
Business transparency: Corporate law promotes transparency and accountability in organizations by requiring companies to keep accurate records, disclose financial information, and hold regular meetings.
Investor confidence: Clear and consistent corporate rules increase investor confidence in the business environment. Investors can invest in companies that operate within a well-defined legal framework.
Corporate Governance: Corporate law establishes principles of corporate governance that help maintain ethical standards, prevent fraud and mismanagement, and ensure the longevity of business
Question:2 What are the objectives of Company Law?
Answer: Company law serves as a framework for establishing procedures and rules for business management and business formation, operation and winding up of companies. The objective is multifaceted. Designed to ensure compliance Protect stakeholders Improve transparency and accountability and improve business efficiency By creating a legal framework for corporate governance.
Corporate law therefore protects the rights of shareholders, creditors, employees and other stakeholders. It also aims to prevent fraud. incorrect management and misconduct in the company through the legal work of directors and officers. and to create monitoring and accountability procedures.
Corporate law also promotes social responsibility and sustainable business practices. By encouraging companies to consider their impact on people and the environment. Corporate law promotes the stability and integrity of the business environment through effective problem resolution and enforcement of ethical standards. Ensuring fairness and justice for all stakeholders
Question:3 What are the types of companies?
Types of Company Law
- Companies Limited by Shares.
- Companies Limited by Guarantee.
- Unlimited Companies.
- One Person Companies (OPC)
- Private Companies.
- Public Companies.
- Holding and Subsidiary Companies.
- Associate Companies
Question:4 What are the features of company?
Answer :
Limited Liability: The liability of the members is limited to the amount invested in the company. Their personal assets are often secured by the debts and liabilities of the company.
Continuous Succession: There is continuous succession in the company. This means that their lives are not dependent on the lives of their members or leaders. Ability to continue the business despite a change in ownership or management.
Transfer of shares: Ownership of a company can be easily changed by buying and selling shares in the capital of the company.
Separate management: The company is managed and operated by directors and officers who are separate from the shareholders.
Centralized management: The company is managed by a board of directors usually elected by the shareholders. The board of directors makes important decisions on behalf of the company and appoints officers to manage the day-to-day operations.
Generic Seal: Most companies have a generic seal. It is used to document and represent the company’s contractual obligations and legal obligations.