What is cost Accounting meaning and objectives or concepts and types

Cost Accounting Introduction
Cost accounting is the process of determining and accumulating the cost of a product or activity, it is a process of accounting for the incurrence and the controls of cost. it also covers classification, analysis, and
interpretation of cost. In other words, it is a system of accounting that provides information about the ascertainment, and controls of product costs.
Or services it measures the operating efficiency of the enterprise. it is an internal aspect of the organization is accounting for cost aimed at providing cost data, statements, and reports for managerial decision-making.
what is cost Accounting?
Cost accounting is a financial method that involves tracking and controlling expenses incurred by a business in producing and selling its products or services.
It plays an important role in providing businesses with detailed information on costs including raw materials, labor, and overheads, helping to make informed decisions and manage costs effectively.
For example, a manufacturing company may use to identify the specific costs associated with producing each unit of product for better financial planning and resource allocation.
Cost Accounting Institutes
- institute of Cost Accountants of India (ICAI):
- Formerly known as the Institute of Cost and Works Accountants of India (ICWAI), it is now named the Institute of Cost Accountants of India (ICAI). This institute is a premier professional body in India that offers courses and certifications in cost and management accounting.
- Chartered Institute of Management Accountants (CIMA):
- Based in the United Kingdom, CIMA is a globally recognized professional body that focuses on management accounting. While not exclusively cost accounting, CIMA covers a broader range of topics related to financial management and strategic decision-making.
Scope of cost Accounting
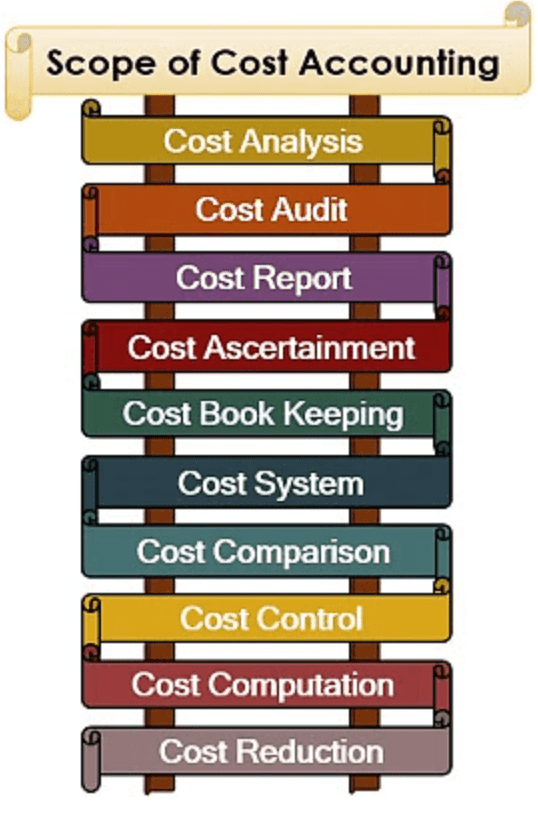
- Cost analysis
- Cost audit
- Cost Ascertainment
- Cost bookkeeping
- cost system
- Cost Comparison
- Cost control
- cost computation
- cost reduction
Explanation
- Cost Analysis:
- Cost analysis involves the systematic examination and evaluation of the costs associated with a specific activity, process, or project. It aims to understand, classify, and interpret various costs to make informed decisions.
- Cost Audit:
- Cost audit is an examination of a company’s cost accounting records, systems, and procedures to ensure they comply with regulatory standards. It helps in verifying the accuracy of cost information and adherence to cost accounting principles.
- Cost Ascertainment:
- Cost ascertainment is the process of determining and calculating the total cost incurred in the production of goods or services. It involves identifying and collecting all relevant costs associated with a particular product or activity.
- Cost Bookkeeping:
- Cost bookkeeping refers to the systematic recording and documentation of all costs incurred by a business. It involves maintaining detailed records of expenses, which helps in tracking and controlling costs effectively.
- Cost System:
- A cost system is a set of procedures and methods used by a company to accumulate, allocate, and control costs. It establishes a framework for capturing and analyzing costs to aid in managerial decision-making.
- Cost Comparison:
- Cost comparison involves evaluating the costs of similar products, processes, or alternatives to identify the most cost-effective option. It helps in making decisions that minimize expenses while achieving desired outcomes.
- Cost Control:
- Cost control is the management process of regulating and managing costs within a predetermined budget. It involves setting standards, monitoring performance, and taking corrective actions to ensure expenses stay within acceptable limits.
- Cost Computation:
- Cost computation is the process of calculating the total cost of producing a specific product or service. It includes the aggregation of direct and indirect costs to determine the overall cost of production.
- Cost Reduction:
- Cost reduction involves the identification and elimination of unnecessary expenses while maintaining the quality and efficiency of products or services. It aims to increase profitability by optimizing resource utilization.
The terms costing and cost accounting are often used interchangeably. however, the scope of cost accounting is broader than that of costing.
Cost Accounting difference between cost accounting and financial accounting
| objective | cost accounting | financial accounting |
| Purpose | Cost Accounting: Helps businesses track and control their costs. It focuses on internal management needs to improve efficiency. | Financial Accounting: Aims to provide information to external parties like investors, creditors, and regulatory authorities. It summarizes the financial position of a company. |
| Focus | Cost Accounting: Concentrates on specific products, services, or activities within the organization. It’s more detailed and specific. | Financial Accounting: Looks at the overall financial health of the entire company. It provides a broader picture. |
| Period time | Cost Accounting: Emphasizes short-term analysis for immediate decision-making. | Financial Accounting: Focuses on long-term financial performance and stability. |
| Reporting | Cost Accounting: Generates detailed reports on costs associated with specific projects, products, or departments. | Financial Accounting: Produces general-purpose financial statements like the balance sheet and income statement. |
Cost Accounting Objectives
There is a relationship between the information needs of management, objectives and techniques and tools used for analysis in cost accounting.

Cost accounting has the following main objectives to serve ‘
- Determining selling price
- controlling cost
- providing information for decision-making
- Ascertaining costing profit
- facilitating the preparation of financial and other statements
Explanation
Determine the selling price:
Definition: Determining how much must be paid for a product or service in order for the company to make money. It’s like deciding the right price to sell something.
Price of control:
Description: Managing and tracking how much money is spent on various items. It’s like you’re spending less.
Provide information for decision-making:
Definition: To provide details and facts to help people make informed choices. It’s like providing useful information so that decisions can be made intelligently.
Cost advantage information:
Definition: Determine the amount of cash remaining after accounting for all costs associated with manufacturing and selling a product. Like knowing how much money you make.
Assist in the preparation of financial statements and other accounts:
Description: To facilitate the creation of records showing sound business results, including financial statements. It seems to make it easier to prepare reports on the company’s activities.
Cost Accounting difference between cost accounting and management accounting
| Objective | Cost accounting | management accounting |
| Focus | Focus: Deals with keeping track of how much it costs to make a product or run a | Focus: Look at the bigger picture, not just costs, but also other info to help make important decisions. |
| Information | Information: Gives detailed info about specific costs and helps control them | Information: Provides a full view, including money and other details, for decisions affecting the whole company. |
| users | Users: Used by people inside the company to manage costs for a particular thing. | Users: Used by managers at different levels to decide what’s best for the entire organization. |
Important Points of Cost Accounting
Tracking cost:
What it is: Pay attention to where businesses spend money.
Why it’s important: It helps you understand what’s costing you money and where it’s going.
Please help:
What it is: Splitting costs into components such as raw materials, labor, and other costs.
Why it’s important: Be transparent about all expenses.
Payment assistance order:
What it does: Provides information for cost and value decision making.
Why it matters: Guide your business in making choices that will save money or increase profits.
Career Research:
What it is: Find out if your business is using resources wisely.
Why it’s important: Helps you be more efficient and reduce unnecessary costs.
Financial Planning:
What it is: Plan to earn more than you spend.
Why it’s important: To ensure long-term profitability of the business.
Types of Cost Accounting
- Job Costing:
- What it is: Like counting the cost for each specific job or project.
- Example: Building a house or making a custom piece of furniture.
- Process Costing:
- What it is: Counting costs for making lots of similar things altogether.
- Example: Making tons of cookies or producing bottles of soda.
- Activity-Based Costing (ABC):
- What it is: Counting costs based on what activities use up resources.
- Example: Figuring out costs by looking at different tasks in a business.
- Standard Costing:
- What it is: Setting standard (expected) costs and then seeing how real costs compare.
- Example: Deciding how much making one product should cost and then checking if it matches the actual cost.
- Marginal Costing:
- What it is: Focusing on how costs change when you make more or less of something.
- Example: Checking how much more it costs to make one extra item.
Question and Answer
Question:1 What do you mean by cost accounting?
Answer: Cost accounting is a financial method used by businesses to track, analyze, and manage the expenses associated with producing and selling goods or services. It involves breaking down costs into various components such as raw materials, labor, and overhead, providing insights into where money is spent. The goal of cost accounting is to help businesses make informed decisions, control expenses, and ensure efficient use of resources, ultimately contributing to better financial management and profitability.
Question:2 What are the 4 types of cost?
Answer:
- Fixed Costs:
- Definition: Costs that remain constant irrespective of the level of production or sales.
- Example: Rent, salaries of permanent staff.
- Variable Costs:
- Definition: Costs that vary in direct proportion to changes in production or sales.
- Example: Raw materials, direct labor.
- Semi-Variable Costs:
- Definition: Costs that have both fixed and variable components.
- Example: Utilities, where there’s a fixed basic charge plus a variable component based on usage.
- Total Costs:
- Definition: The sum of all fixed and variable costs incurred in the production of goods or services.
- Calculation: Total Cost = Fixed Costs + Variable Costs.
Question:3 What is the main purpose of cost accounting?
Answer: ascertain the cost of production for every process, department or service of a business.
Question:4 What is called cost?
Answer: Cost, in a business context, refers to the total expenditure incurred by an organization to produce and deliver goods or services. It encompasses various elements such as raw materials, labor, overhead, and other expenses associated with the production process. Understanding and analyzing costs is crucial for businesses to make informed decisions, set prices, manage resources efficiently, and ensure profitability.
Question:5 What fixed cost means?
Answer: Fixed cost refers to the expenses that remain constant within a certain range of production or business activity, regardless of the quantity of goods or services produced. These costs do not vary with changes in production levels or sales. Fixed costs are incurred even if a business produces nothing or experiences fluctuations in its output.
Conclusion
In short, cost accounting is like a money detective, helping companies understand where their money is going. By cutting costs, supporting goals, and ensuring efficient use of resources, it enables companies to stay smart with their spending.
Gloria Sims
please tell me in english or hindi